In my last post I covered vRealize Operations Manager (vROPS) components and its architecture. Now I will focus more on real world scenario and present deployment options for two datacenters – multi availability zones deployment.
Requirements:
- Design must cover two datacenters.
- Solution must be highly available and perform data gathering and analytics even when one component fails.
- Solution must be available for user interactions and administration even when one component fails.
Assumptions:
- At least vROPS Advanced license. Worth to note that, regardless of your vSphere licence type, when buying VMware vSphere with Operations Management you always get Standard version. So if you have vSphere Enterprise Plus with OM licence you still get vROPS Standard edition. Built-in high availability (automated failover of vROPS nodes) is included only in Advanced or Enterprise license.
- vROPS 6.7, but design is also valid with previous versions.
- Two vCenter Servers, each in one datacenter. No stretched storage clusters.
Design considerations
Scalability
In a single-node installation, the master node manages itself, has adapters installed on it, and performs all data collection and analysis. If you need to gather data from vast amount of objects and perform complicated analysis you can scale up you installation by installing larger nodes or scale out by adding additional data notes. VMware offers Extra Small, Small, Medium, Large, and Extra Large node configurations during installation. vROPS supports up to 240,000 monitored resources spread across six extra large analytic nodes. To get more information how to scale your environment you should read this KB article. Quick tips are:
- Scale up, not out. Use the configuration which has the least number of nodes.
Example: For 180000 objects, deploy as 4 Extra Large nodes instead of 12 Large nodes. You will save half the CPU. - You can increase RAM size instead of increasing both RAM and CPU. This is useful if the number of objects is close to the upper limit. Check that there is enough RAM on the underlying hardware.
- No mixing of nodes with different sizes.
Availability
Master node HA
You can protect vROPS master node by deploying master replica. It is done by converting a data node into a replica of the master node. With HA, data stored on the master node is always 100% backed up on the replica node. If the master node fails, replica is promoted to master and its complete responsibility is taken over. In case the master node failed due to a hardware failure and is back online with the help of vSphere HA, old master node will be configured as the replica node thereafter.
Data node HA
The cluster can recover from a data node failure because redundant services and data are maintained on the other nodes in the cluster. If the data node fails, then the owning resources of that node are promoted on the surviving nodes which have a replica copy of these resources. The new owning node is responsible for collection of data from here onwards. If a data node has failed due to hardware failure and vSphere HA brings it back on a surviving ESXi node in the vSphere cluster, then this node automatically joins the vROPS cluster and the data points are synced.
Remote collector HA
To protect remote collectors you can deploy multiple appliances in collector group. When one collector fails, and the collector is part of a group, adapter workload is redistributed to other collectors.
UI Availability
You can access and interact with the product by using the product UI available on the master and data nodes and also on master replica. If it fails, load balancer can redistribute traffic to survived nodes. Setting up load balancer in front of vROPS nodes has also other benefits:
- Ensures that the deployed cluster is properly balanced for performance of UI traffic and all nodes in the cluster equally participate in the handling of UI sessions.
- Provides simpler access for the users. Instead of accessing each node individually the user only needs one URL to access the entire cluster and not be concerned with which node is available.
Best practices
VMware give set of recommendation that you should follow during your vROPS design. Most important for multi AZ design are:
- Deploy analytics nodes in the same vSphere Cluster. If you cannot deploy analytic nodes in the same vSphere cluster, you must deploy them in the same geographical location. vRealize Operations Manager does not support deploying analytics nodes in multiple geographical locations.
- Each analytics node must be located on the same VLAN and IP subnet, and VLAN cannot be stretched between data centers.
- Latency between analytics nodes cannot exceed 5 milliseconds, and the bandwidth must be equal to or higher than 1 GB per second. It is recommended that bandwidth be 10 GB per second at minimum.
- Deploy analytics nodes on storage of the same type.
- Depending on the size and performance requirements for analytics nodes, apply Storage DRS AntiAffinity rules to ensure that nodes are on separate datastores.
- If you deploy analytics nodes into a highly consolidated vSphere cluster, configure resource reservation to ensure optimal performance. Ensure that the virtual CPU to physical CPU ratio is not negatively impacting the performance of analytic nodes by validating CPU ready time and CPU costop.
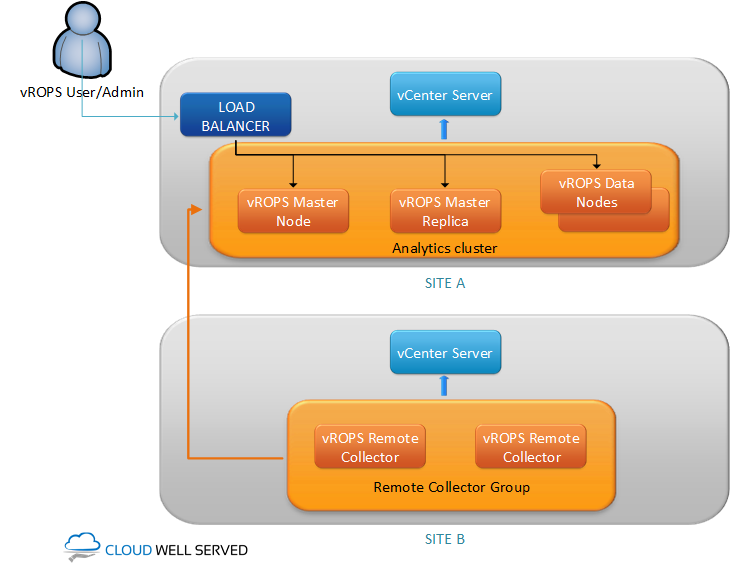
Option 1: One vROPS cluster with remote collectors
To design highly available vROPS solution for multiple datacenters we can deploy analytics cluster in one location and remote collectors in remote site. This is common scenario when we have one main DC and many ROBO sites. This approach works also with two main datacenters. You must remember thought, that failure of whole first site means that you wont be able to access vROPS at all.
It is recommended that latency between sites is less than 200ms. When latency exceeds 200ms, it is recommended that you monitor collections to validate that they are completing in less than 5 minutes. If collections are not completed in this time limit, increase the interval from standard 5 minutes to for example 10 minutes.
| Design element | Design decision | Justification | Implications |
| vROPS architecture | vROPS analytics cluster on first site, vROPS collectors on second site. | No need to perform separate deployment on each site. Single pane of glass for management. | Latency between sites should be less than 200ms for best performance. Failure of whole first site will cause that vROPS will not be available. |
| vROPS cluster availability | Deploy master and master replica node. | Better resiliency for master node. | Another node to be deployed. |
| vROPS UI availability | Deploy vROPS behind load balancer. | Better resiliency for UI. User can always connect to one Virtual IP/Name. UI traffic is redistributed across all nodes. |
External load balancer is required. |
| vROPS scalability | vROPS scaled up or out according to number of objects. | To be able to analysis required number of objects. | Higher number of nodes or bigger nodes deployed. |
| Remote collector | Remote collectors deployed in a group. | Better resiliency in case one collector fails. | More appliances to deploy on second site. |
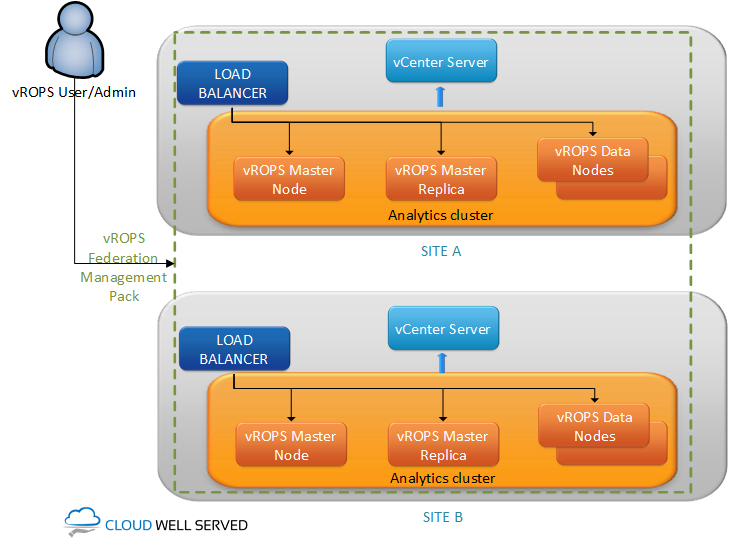
Option 2: Separate vROPS cluster for each site
Other possibility includes two vROPS clusters and suits scenarios when you have:
- really vast amount of objects in each datacenter (more than 32 000), which remote collector are not able to cover
- high latency between sites (more than 200 ms) or to low bandwidth to send data across
- you want higher resiliency between sites and vROPS available for second site in case first site is down
Downside of that approach can be lack of single pane of glass for management. To overcome that I found Federation Management Pack that provides summarized view for both vROPS installations. Unfortunately I didn’t get a chance to test it yet so I’m not sure what exact capabilities it has. You can find info here.
| Design element | Design decision | Justification | Implications |
| vROPS architecture | Two vROPS clusters, one for each site. | Vast amount of objects on remote site. High latency between sites. Higher resiliency for vROPS cluster. |
Two separate installations of vROPS needed. No single pane of glass without Federation Management Pack. |
| vROPS cluster availability | Deploy master and master replica node. | Better resiliency for master node. | Another node to be deployed. |
| vROPS UI availability | Deploy vROPS behind load balancer. | Better resiliency for UI. User can always connect to one Virtual IP/Name. UI traffic is redistributed across all nodes. |
External load balancer is required. |
| vROPS scalability | vROPS scaled up or out according to number of objects. | To be able to analysis required number of objects. | Higher number of nodes or bigger nodes deployed. |
| vROPS manageability | Federation Management Pack deployed. | Single pane of glass. | Additional pack to install and configure. |
Reference Materials
vROPS 6.7 Reference Architecture
vROPS 6.7 Sizing Guidelines
When and how to scale your monitoring solution?

Like!! I blog frequently and I really thank you for your content. The article has truly peaked my interest.